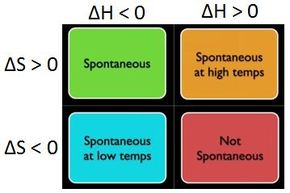
Gibbs Free Energy Spontaneous Chart . Gibbs free energy change and electrical work done in a cell. The symbol g is given for gibbs free energy.
Structural Biochemistry/Enzyme/Gibbs Free Energy Graph - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open World from en.wikibooks.org
See also standard enthalpy of formation, gibbs free energy of formation, entropy and molar heat capacity of organic substances and thermodyamics key values internationally. This size is convenient for driving many biochemical processes in your body. The symbol g is given for gibbs free energy.
Structural Biochemistry/Enzyme/Gibbs Free Energy Graph - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open World
N2o4 (g) → 2 no2 (g) the standard enthalpy of this reaction is 57.2 kj and its standard entropy is 175.61 j/k. If δ r g o < 0 the. The symbol g is given for gibbs free energy. Under such conditions the decrease in gibbs free energy equals the maximum amount of energy available for work, whereas if it increases for some transition, the change in gibbs free energy represents the minimum amount of work required.
Source: www.khanacademy.org
When atp reacts with water (hydrolysis) energy is released: It is defined by the gibbs equation: Evaluating gibbs free energy is much simpler: With the change to the chart described in the passage, we know that the system is losing heat from reactants to products (5 is lower than 1). The table below shows the standard enthalpy of formation, the.
Source: www.quora.com
It is easy as long as you remember to convert the entropy change value into kj. Gibbs free energy change, ∆g gibbs free energy is a term that combines the effect of enthalpy and entropy into one number the balance between entropy and enthalpy determines the feasibility of a reaction. The gibbs free energy gives the maximum amount of work.
Source: equithermoiqas.weebly.com
Enthalpy is the thermodynamic quantity equivalent to the total heat content of a. G, can be ideally considered as “standard free energy charge”. The formula for gibbs free energy is written in terms of δh° and δs° along with temperature: And therefore we have derived from the 2nd law of thermodynamics: When atp reacts with water (hydrolysis) energy is released:
Source: www.blendspace.com
Intuition behind why spontaneity is driven by enthalpy, entropy and temperature. I would like to know if the process is non. With the change to the chart described in the passage, we know that the system is losing heat from reactants to products (5 is lower than 1). Gibbs free energy change and electrical work done in a cell. This.
Source: www.cliffsnotes.com
The easiest way to understand this situation while solving an equation is if g is negative, then it is spontaneous. Since we know that the change in the gibbs free energy, δ r g o, between products and reactants tells us whether or not the reaction will run spontaneously we will need this quantity at the new temperature. This value.
Source: www.studyorgo.com
Gibbs free energy change and electrical work done in a cell. Introduction • in this chapter, we look more closely at what causes chemical change. Since we know that the change in the gibbs free energy, δ r g o, between products and reactants tells us whether or not the reaction will run spontaneously we will need this quantity at.
Source: kwokthechemteacher.blogspot.com
Gibbs free energy change, ∆g gibbs free energy is a term that combines the effect of enthalpy and entropy into one number the balance between entropy and enthalpy determines the feasibility of a reaction. Free energy and free energy change —the gibbs free energy, g, is used to describe the spontaneity of a process. Some reactions are spontaneous because they.
Source: www.crediblehulk.org
This value is the combination of enthalpy (h) and entropy (s). It is easy as long as you remember to convert the entropy change value into kj. A) the change of the gibbs free energy at 25 °c. Driving forces and gibbs free energy. • most simply, it can be described as “energy spreads out.” i.
Source: en.wikibooks.org
Sodium and water in a spontaneous reaction. A) the change of the gibbs free energy at 25 °c. With the change to the chart described in the passage, we know that the system is losing heat from reactants to products (5 is lower than 1). In this video, we're going to talk about what the change in gibbs free energy,.
Source: www.cliffsnotes.com
Gibbs free energy and temperature: The formula for gibbs free energy is written in terms of δh° and δs° along with temperature: Gibbs free energy change, ∆g gibbs free energy is a term that combines the effect of enthalpy and entropy into one number the balance between entropy and enthalpy determines the feasibility of a reaction. Spontaneity • thermodynamics allows.
Source: www.khanacademy.org
This heat is going out of. It is defined by the gibbs equation: Free energy and free energy change —the gibbs free energy, g, is used to describe the spontaneity of a process. Created by sal khan.watch the next lesson. I would like to know if the process is non.
Source: www.youtube.com
Is the reaction spontaneous at 25 °c? The transformation of a system from one state to another, at constant temperature and pressure, is spontaneous if the gibbs free energy. The gibbs free energy is calculated from si unit j (joules). Gibbs free energy and temperature: Atp can release gibbs free energy in packets of 30.5 kj for each atp converted.
Source: users.stlcc.edu
Under such conditions the decrease in gibbs free energy equals the maximum amount of energy available for work, whereas if it increases for some transition, the change in gibbs free energy represents the minimum amount of work required. Therefore, the gibbs free energy symbol, i.e. • we will see that everything comes back to entropy, and we seek to understand.
Source: www.tectechnicsclassroom.tectechnics.com
This is given by the relationship : So if you had to calculate the gibbs free energy change at, say, 298 k, you can just slot the numbers in: When a process occurs at constant temperature and pressure , we can rearrange the second law of thermodynamics and define a new quantity known as gibbs free energy: The equation is.
Source: chem.libretexts.org
In this video, we're going to talk about what the change in gibbs free energy, or delta g as it's most commonly known is, and what the sign of this numerical value tells us about the reaction. The transformation of a system from one state to another, at constant temperature and pressure, is spontaneous if the gibbs free energy. Now,.
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Free energy and free energy change —the gibbs free energy, g, is used to describe the spontaneity of a process. If δ r g o < 0 the. Equation 1 relates the gibbs free energy change to the entropy and enthalpy changes for a reaction. It is defined by the gibbs equation: Therefore, the gibbs free energy symbol, i.e.
Source: ibalchemy.com
In this video, we're going to talk about what the change in gibbs free energy, or delta g as it's most commonly known is, and what the sign of this numerical value tells us about the reaction. Equation 1 relates the gibbs free energy change to the entropy and enthalpy changes for a reaction. Gibbs free energy change and electrical.
Source: chem.libretexts.org
Equation 1 relates the gibbs free energy change to the entropy and enthalpy changes for a reaction. A negative value for gibbs free energy indicates a spontaneous reaction. Spontaneity • thermodynamics allows us to predict which processes will occur spontaneously. The formula for gibbs free energy is written in terms of δh° and δs° along with temperature: Gibbs free energy.
Source: lavelle.chem.ucla.edu
The formula for gibbs free energy is written in terms of δh° and δs° along with temperature: Is the reaction spontaneous at 25 °c? Evaluating gibbs free energy is much simpler: This size is convenient for driving many biochemical processes in your body. The table below shows the standard enthalpy of formation, the standard gibbs free energy of formation, standard.
Source: www.youtube.com
A negative value for gibbs free energy indicates a spontaneous reaction. Driving forces and gibbs free energy. Created by sal khan.watch the next lesson. Here, n is the number of moles of electrons transferred in the balanced equation for the reaction occurring in the cell. Enthalpy is the thermodynamic quantity equivalent to the total heat content of a.