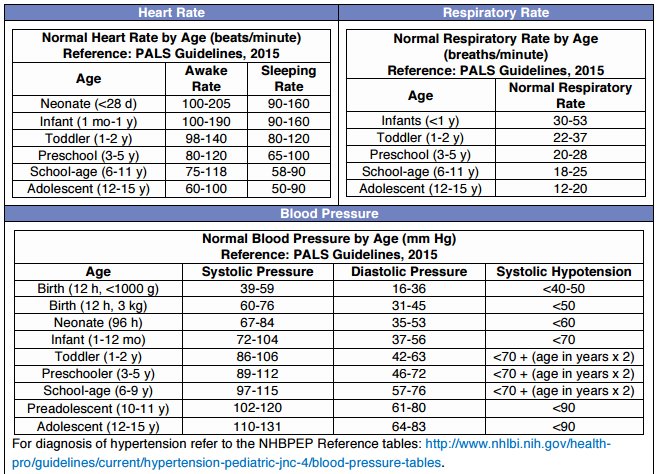
Normal Vital Signs Chart . 60 to 100 beats per minute. Mucous membranes of the mouth:
Pediatric Vital Signs – Learn Em from learnem.org
80 to 100 beats per minute: These vital signs are the correct vital signs to use for the nremt exam. Vital signs provide essential data for determining the severity of illnesses, injuries or emergencies.
Pediatric Vital Signs – Learn Em
15 to 30 breaths per minute. 60 to 100 beats per minute. 80 to 100 beats per minute: What are the four main vital signs?
Source: www.studocu.com
12 to 15 breaths per minute resting. 97.8°f to 99.1°f (36.5°c to 37.3°c); 80 to 100 beats per minute. Pediatric vital signs reference chart pedscases. However, vital signs are not always correctly recorded or appropriately acted upon (3, 6, 9, 10, 14).
Source: www.pinterest.com
This will vary between age, 12 to 18 breaths per minute. The noc will also provide a single view of clinical information and assist in recognising future trends, which may. 60 to 100 beats per minute. • between 120/80mmhg to 90/60mmhg = normotension (normal blood pressure).
Source: iastate.pressbooks.pub
Medical professionals use these four measurements in numerous ways, and variations from normal adult vital signs can prove to be important in assessing one’s general health, indicating disease, and monitoring the. 12 to 20 breaths per minute. Mucous membranes of the mouth: Infant vital signs (age 1 to 12 months) 15 to 30 breaths per minute:
Source: www.tomwademd.net
Child vital signs (age 1 to 8 years) pulse: Pulse • the wave of blood created by the heart pumping as it travels along arteries Infant vital signs (age 1 to 12 months) 60 to 100 beats per minute. The new zealand early warning score (nzews) is.
Source: www.reddit.com
We identified it from trustworthy. These vital signs are the correct vital signs to use for the nremt exam. 60 to 100 beats per minute. Use this equine vital signs chart to record your horse’s health information and establish a baseline for normal health data. 12 to 15 breaths per minute resting.
Source: learnem.org
90/60 mm hg to 120/80 mm hg. 15 to 30 breaths per minute: • between 120/80mmhg to 90/60mmhg = normotension (normal blood pressure). 90 to 140 mmhg (systolic) 60 to 90 mmhg (diastolic) respirations: The new zealand early warning score (nzews) is.
Source: www.grepmed.com
The national vital signs chart and early warning score provide a safety net for adult patients who acutely deteriorate while in hospital. The newborn observation chart (noc) is a vital signs chart, which has been developed to standardise the initial assessment, and care of newborn babies in new zealand. Child vital signs (age 1 to 8 years) pulse: Medical professionals.
Source: www.researchgate.net
90 to 140 mmhg (systolic) 60 to 90 mmhg (diastolic) respirations. 12 to 18 breaths per minute. 90/60 mm hg to 120/80 mm hg. 28 to 40 beats per minute resting heart rate. 12 to 15 breaths per minute resting.
Source: studylib.net
12 to 18 breaths per minute. Pediatric vital signs reference chart pedscases. Pulse • the wave of blood created by the heart pumping as it travels along arteries We identified it from trustworthy. 80 to 100 beats per minute:
Source: www.coursehero.com
However, vital signs are not always correctly recorded or appropriately acted upon (3, 6, 9, 10, 14). • 140/90mmhg and above = hypertension (high blood pressure). Vanessa harvey a vital signs monitor. Page 1 of 1 * excluding patients with congenital cardiac conditions who have oxygen saturations lower normally mean bp thresholds at 3rd percentile according to post conceptual age.
Source: www.nucleotype.com
Below is a list of normal vital signs for each age range and gender. 60 to 100 beats per minute. In most medical settings, the four standard primary vital signs are as follows: Normal vitals for an adult horse: 12 to 18 breaths per minute.
Source: www.researchgate.net
What are the four main vital signs? Moist, light pink to “bubblegum pink” color. 80 to 110 mmhg systolic. All of these factors increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and other serious health complications. 12 to 18 breaths per minute.
Source: twitter.com
Medical professionals use these four measurements in numerous ways, and variations from normal adult vital signs can prove to be important in assessing one’s general health, indicating disease, and monitoring the. These vital signs are the correct vital signs to use for the nremt exam. If another risk category is identified which is not currently. Below is a list of.
Source: www.templateroller.com
15 to 30 breaths per minute. They also help you communicate quickly and efficiently with your equine health care professionals. Child vital signs (age 1 to 8 years) pulse. 90 to 140 mmhg (systolic) 60 to 90 mmhg (diastolic) respirations. Medical professionals use these four measurements in numerous ways, and variations from normal adult vital signs can prove to be.
Source: www.medicalestudy.com
80 to 100 beats per minute. Medical professionals use these four measurements in numerous ways, and variations from normal adult vital signs can prove to be important in assessing one’s general health, indicating disease, and monitoring the. All of these factors increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and other serious health complications. Pupils that are midpoint, equal in size.
Source: www.pedscases.com
97.8°f to 99.1°f (36.5°c to 37.3°c); Child vital signs (age 1 to 8 years) pulse. Child vital signs (age 1 to 8 years) pulse. Pulse • the wave of blood created by the heart pumping as it travels along arteries In most medical settings, the four standard primary vital signs are as follows:
Source: www.youtube.com
12 to 20 breaths per minute. Moist, light pink to “bubblegum pink” color. If another risk category is identified which is not currently. 80 to 110 mmhg systolic. Child vital signs (age 1 to 8 years) pulse.
Source: www.pinterest.com
Child vital signs (age 1 to 8 years) pulse. 60 to 100 beats per minute. 97.8°f to 99.1°f (36.5°c to 37.3°c); 80 to 110 mmhg systolic. Page 1 of 1 * excluding patients with congenital cardiac conditions who have oxygen saturations lower normally mean bp thresholds at 3rd percentile according to post conceptual age post conceptual
Source: www.emt-national-training.com
Disease, drug therapies, or other factors cause their vital signs to fall outside of the normal range on the national vital signs chart. Child vital signs (age 1 to 8 years) pulse. May 17, 2018 by michael nemergut, m.d., ph.d. Mucous membranes of the mouth: 12 to 15 breaths per minute resting.
Source: www.pinterest.com
60 to 100 beats per minute. Disease, drug therapies, or other factors cause their vital signs to fall outside of the normal range on the national vital signs chart. These vital signs are the correct vital signs to use for the nremt exam. 12 to 18 breaths per minute. Vital signs provide essential data for determining the severity of illnesses,.